|

- Questions -

 1-1 : What is
AGP? 1-1 : What is
AGP?
 1-2 : What are
the key benefits of AGP? 1-2 : What are
the key benefits of AGP?
 1-3 : What are
AGP 1x and AGP 2x? 1-3 : What are
AGP 1x and AGP 2x?
 1-4 : What is
SBA? 1-4 : What is
SBA?
 1-5 : What is
Pipelining? 1-5 : What is
Pipelining?
 1-6 : What is
DIME? 1-6 : What is
DIME?
 1-7 : What is
"AGP memory"? 1-7 : What is
"AGP memory"?
 1-8 : What is
GART? 1-8 : What is
GART?
 1-9 : Which
applications will benefit from AGP? 1-9 : Which
applications will benefit from AGP?
 1-10 : Will
AGP replace PCI? 1-10 : Will
AGP replace PCI?
 1-11 : Must I
have a Pentium II for AGP? 1-11 : Must I
have a Pentium II for AGP?
 1-12 : What
are the main benefits of an Intel® Pentium® II / 440LX AGPset system? 1-12 : What
are the main benefits of an Intel® Pentium® II / 440LX AGPset system?
 1-13 : Why is
AGP faster compared to PCI? 1-13 : Why is
AGP faster compared to PCI?
 1-14 : Should
I have 2 MB, 4 MB or more Frame Buffer Memory on my AGP graphics card? 1-14 : Should
I have 2 MB, 4 MB or more Frame Buffer Memory on my AGP graphics card?
 1-15 : Which
kind of memory should be on the motherboard? 1-15 : Which
kind of memory should be on the motherboard?
 1-16 : Which
operating system supports AGP today? 1-16 : Which
operating system supports AGP today?
 1-17 : Can I
use my PCI graphics card with an AGP motherboard? 1-17 : Can I
use my PCI graphics card with an AGP motherboard?
 1-18 : Does
AGP also speed up MS-DOS applications? 1-18 : Does
AGP also speed up MS-DOS applications?
 1-19 : Must
the system BIOS support AGP? 1-19 : Must
the system BIOS support AGP?
 1-20 : What's
next in the evolution of AGP? 1-20 : What's
next in the evolution of AGP?
 1-21 : Can I
use my Monster 3D with an AGP graphic card? 1-21 : Can I
use my Monster 3D with an AGP graphic card?
 1-22 : Should
I buy an AGP graphics card now? 1-22 : Should
I buy an AGP graphics card now?
 1-23 : Will
special applications for AGP graphics come up? 1-23 : Will
special applications for AGP graphics come up?
 1-24 : What
are the software requirements for an AGP-based system? 1-24 : What
are the software requirements for an AGP-based system?
 1-25 : How
can I verify my system for the AGP software requirements? 1-25 : How
can I verify my system for the AGP software requirements?

- Answers -

1-1 : What is AGP? 
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is a dedicated 66 MHz high-speed interface between the
motherboard chipset and the graphics controller on the graphics subsystem. The AGP
interface specification allows the graphics subsystem access to dynamically allocated
portions of system main memory. From the other side, the CPU can access this so-called AGP
memory much faster than sending data over the PCI bus into the frame buffer of the
graphics subsystem. This system memory can be used for storing large texture maps and
executing texture manipulation commands by the graphics subsystem's direct memory execute
(DIME).
1-2 : What are the key benefits of AGP? 
- The peak bandwidth of AGP is four times higher (AGP 2X) than on the PCI bus.
- Direct execution of texture maps from system memory vs. requiring textures to be
pre-loaded into local video memory via the PCI bus.
- Less PCI bus congestion.
- Improved system concurrency for balanced PC performance. The system processor can
perform other activities while the graphics chip is accessing texture data in system
memory.
- Saves one PCI slot.
1-3 : What are AGP 1x and AGP 2x? 
The AGP is basically twice as fast as the PCI bus. The AGP specification specifies the
66MHz operation of AGP 1x. The AGP has the ability to transfer data on both the rising and
falling edges of the clock signal. This doubles the data throughput once again. This
operation is called AGP 2x and can transfer 528 MByte per second. AGP 2x is only
functional with SBA. Intel® is currently working on an even higher performance mode for
AGP, called AGP 4x mode. It will be incorporated into the next revision of the AGP
specification and is targeted primarily at workstations and other high-performance
platforms.
1-4 : What is SBA? 
SBA means Side Band Addressing. In addition to the 32-bit data path, there is an 8-bit
control channel. The AGP graphics card can send commands over the control channel even
while the host transfers data over the data path. SBA only makes sense with pipelining.
1-5 : What is Pipelining? 
Pipelining is a technique that allows sending of more than one data request sequentially
before the first request can be served with data. On the PCI bus each request must be
served with data before the next request can be sent. The time between request and answer
is called latency time and is lost time on PCI. AGP pipelining uses this latency time for
sending requests and is more efficient than PCI.
1-6 : What is DIME? 
DIME (Direct Memory Execute) is the key to real AGP performance. DIME enables the graphic
controller to execute commands directly in the system memory on the motherboard. These are
mainly geometry transformations and filter operations for textures. The benefit of DIME is
that no part of the frame buffer on the graphics card (off-screen memory) must be reserved
for storing texture data. This part of the frame buffer can be used for higher resolution
and / or more colors.
1-7 : What is "AGP memory"? 
"AGP memory" is a portion of system memory dynamically allocated for quick
access by the graphics controller. The CPU is still allowed to write graphics data into
this memory area. Writing there can be done much faster than into the local frame buffer
via the PCI bus. The latest applications may need anywhere from 2 MB up to 16MB or more
for texture storage; by using AGP memory, they can get it.
1-8 : What is GART? 
GART (Graphics Address Remapping Table) is a so-called built-in hardware in the
motherboard chipset, to allow the graphics controller and its software to see a contiguous
space in main memory, when in fact the pages are disjointed.
1-9 : Which applications will benefit from AGP? 
All Direct3D applications will benefit from the faster AGP interface and the "Direct
Memory Execute" of textures. But new applications written to exploit AGP should see
noticeably speedier 3D with far richer texture content.
1-10 : Will AGP replace PCI? 
No. PCI is a bus system and AGP is a point-to-point interface. Because of the higher clock
rates on AGP, it is not possible to connect more then one device to the chip set. If you
have heard that AGP is a PCI extension, this only reflects the fact that the AGP
specification was based on the PCI specification.
1-11 : Must I have a Pentium II for AGP? 
AGP was first available with Intel® Pentium II CPU and Intel® 440LX chipset. But now we
see chipsets from other vendors, VIA AGP chipset ApolloVP3 for example, for socket 7
Pentium systems. Intel® will not provide a socket 7, Pentium processor based AGP
solution.
1-12 : What are the main benefits of an Intel® Pentium® II /
440LX AGPset system? 
The Intel® Pentium® II with the 440LX AGPset combination delivers the best performance
available today and gets the most benefit out of AGP. The Pentium II processor with its
Dual Independent Bus (DIB) architecture for the L2 cache and the memory subsystem provides
3 times more bandwidth.
1-13 : Why is AGP faster compared to PCI? 
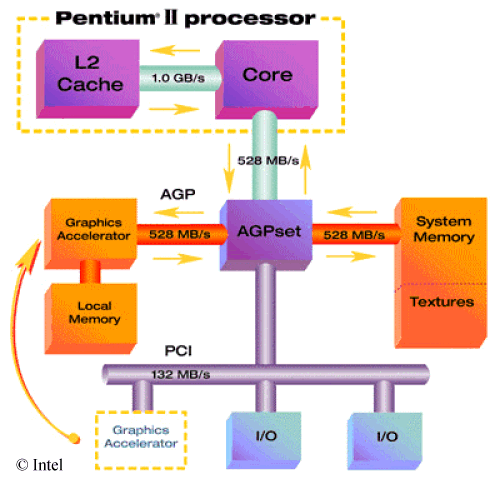
The PCI bus is limited to a maximum bandwidth of 132Mbyte/s. This bandwidth is
not available for the graphics subsystem alone. Other I/O devices such as fast SCSI and
Ethernet controllers occupy 40MB/s and 12.5MB/s respectively. A 3D application, let's say
a game, working with a resolution of 800x600 and 16-bit color depth (HighColor), writing a
scene with 25 frame per second, providing bi-linear texture mapping and z-buffering, needs
a PCI bandwidth of 350MB/s. In this case the PCI bus becomes hopelessly overloaded. The
AGP interface between the add-on graphics accelerator and the AGPset provides a bandwidth
of 528 MB/s (AGP 2x). This is really much more than the PCI bus can ever deliver. The 528
MB/s bandwidth is also available between the Intel® Pentium II processor and the AGPset
and the System Memory and the AGPset.
1-14 : Should I have 2 MB, 4 MB or more Frame Buffer Memory on my
AGP graphics card? 
Let's look at the situation for a PCI graphics card first. For a today's typical PCI
graphics card (2 MB or 4 MB), the table shows you the amount of local frame buffer (LFB)
needed for different resolutions. A 2 MB card will not provide you enough texture RAM. A 4
MB card offers you a typical 800x600 resolution for 3D applications, but the remaining
texture RAM is limited. Only with an expensive 8 MB graphics card does the remaining
texture RAM become meaningful.
With AGP, textures will be stored in system memory. The selection of the amount of frame
buffer for 3D only depends on the resolution used. In general, an inexpensive entry-level
2 MB AGP graphics card could be used for today's 3D applications with large, high-quality
textures. Today's standard for higher 3D resolutions is a graphics card with 4 MB or 8 MB
of local frame buffer.
| 3D Application |
Memory for Front Buffer (16-bit) |
Memory for Back Buffer (16-bit) |
Memory for
Z-Buffer
(16-bit) |
Required Graphics Memory |
Memory of Graphics Board |
Remaining Memory for Textures |
| 640x480 |
600KB |
600KB |
600KB |
1,8 MB |
2 MB |
0,2 MB |
| 800x600 |
0,92MB |
0,92MB |
0,92MB |
2,74 MB |
4 MB |
1,26 MB |
| 800x600 |
0,92MB |
0,92MB |
0,92MB |
2,74 MB |
8 MB |
5,26 MB |
| 1024x768 |
1,5MB |
1,5MB |
1,5MB |
4,5 MB |
8 MB |
3,5 MB |
1-15 : Which kind of memory should be on the motherboard? 
With the Intel® 440LX AGPset on Pentium II motherboards, SDRAM is supported now. This
allows faster data streaming between the Pentium II processor, AGP graphics accelerator
and PCI devices. If you buy a new AGP motherboard, SDRAM is recommended.
1-16 : Which operating system supports AGP today? 
Today, only Windows® 95, OEM Service Release 2.1 supports the AGP features. Windows NT
4.0 does not support AGP features, but if you wish to run NT 4.0 on an AGP motherboard
with an AGP graphic card installed, you need to have Service Pack 3 (SP3) installed.
1-17 : Can I use my PCI graphics card with an AGP motherboard? 
Yes, there is no limitation on using a PCI graphics card with an AGP motherboard. But the
benefits of AGP can only be realized with an AGP graphics card.
1-18 : Does AGP also speed up MS-DOS applications? 
MS-DOS does not support virtual addressing. So GART serves no purpose and some DOS
application driver work would have to be done to turn on direct access to textures in
system memory. The real benefit old applications will see is the faster AGP system speed.
1-19 : Must the system BIOS support AGP? 
Yes, the BIOS on the motherboard must support AGP. Otherwise textures cannot be stored in
system RAM. Check out your motherboard vendor's web site for the latest available BIOS
version and flash it into your system.
1-20 : What's next in the evolution of AGP? 
Today's AGP solution is already a milestone in 3D performance on a PC system.
Nevertheless, AGP 4x will come soon. Intel® is working on doubling the speed of the AGP
interface yet again. On the next generation of AGP motherboards we will see 100MHz SDRAM
(today 66MHz) memories. This will speed up the overall system performance and the graphics
controller to system memory bandwidth. By the end of the century, a new memory technology
with a bandwidth never seen before will be on the motherboards.
1-21 : Can I use my Monster 3D with an AGP graphic card? 
Yes of course you can. Your 3D applications accelerated for the Monster 3D will run as
usual on the Monster. A Direct3D application will take all of the AGP benefits.
1-22 : Should I buy an AGP graphics card now? 
If your system often runs up against its limits with games or other 3D applications, then
it is time to break your limits now. Diamond Multimedia offers you today's best AGP
graphics solutions. Select the graphics card of your choice. If you visit our web sites
frequently, you will see very interesting AGP products.
1-23 : Will special applications for AGP graphics come up? 
Yes, because applications will become optimized for AGP systems, taking full advantage of
the AGP features, and will have large, high-quality textures. These applications will also
run on non-AGP systems, because DirectX 5 provides a set of (texture) memory allocation
mechanisms that work on all system configurations. The disadvantage for a non-AGP system
will be a noticeable performance decrease.
1-24 : What are the software requirements for an AGP-based system? 
- Microsoft® Windows® 95 OSR 2.1 installed
- The GART virtual device driver for your motherboard (e.g. VGART.VXD for Intel®
440LX chip set, or VIA_GART.VXD for VIA Apollo VP3 chipset)
- DirectX 5.0 installed.
1-25 : How can I verify my system for the AGP software
requirements? 
- To verify that you have OSR 2 installed
1. From the START menu, point to SETTINGS and click on CONTROL PANEL.
2. Double-click the SYSTEM control panel.
3. On the GENERAL tab, check that the system version is 4.00.950B.
- To verify that you have OSR 2.1 installed
1. From the START menu, point to SETTINGS and click on CONTROL PANEL.
2. Double-click the ADD/REMOVE Programs control panel.
3. In the list of installed software, check for USB Support. If it's in the list, you have
OSR 2.1 installed.
- To verify the version of the VGART.VXD
1. Use the Windows® Explorer to open the Windows folder and then the System
folder.
2. Locate the file VGART.VXD (or equivalent) and right-click on it to display the shortcut
menu.
3. Click on properties.
4. Click on the Version tab (look for v.1.0.16 for VGART.VXD).
- To verify that you have DirextX 5.0 installed.
1. From the START menu, point to SETTINGS and click on CONTROL PANEL.
2. Double-click the ADD/REMOVE Programs control panel.
3. Double-click on DirectX-Driver.
4. Check you have DirectDraw and Direct3D version 4.05.00.0155 or later.
|